In July 1998, a tragic mid-air collision unfolded in the skies over Quiberon Bay, France, involving Proteus Airlines Flight 706 and a private Cessna 177. This disaster, which claimed the lives of all onboard both aircraft,
serves as a haunting reminder of the risks associated with seemingly minor deviations in flight paths.
In aviation safety circles, the incident underscores the importance of strict adherence to flight plans and the criticality of maintaining constant situational awareness. Here’s a look back at the fatal events of that day, pieced together from various sources.
1:21

Related
Boeing Reaches Settlement In 737 MAX Crash Lawsuit Ahead Of Trial
Boeing made a settlement deal with the family of a victim who died in the 2019 Ethiopian Airlines Boeing 737 MAX crash.
The background: a sightseeing detour
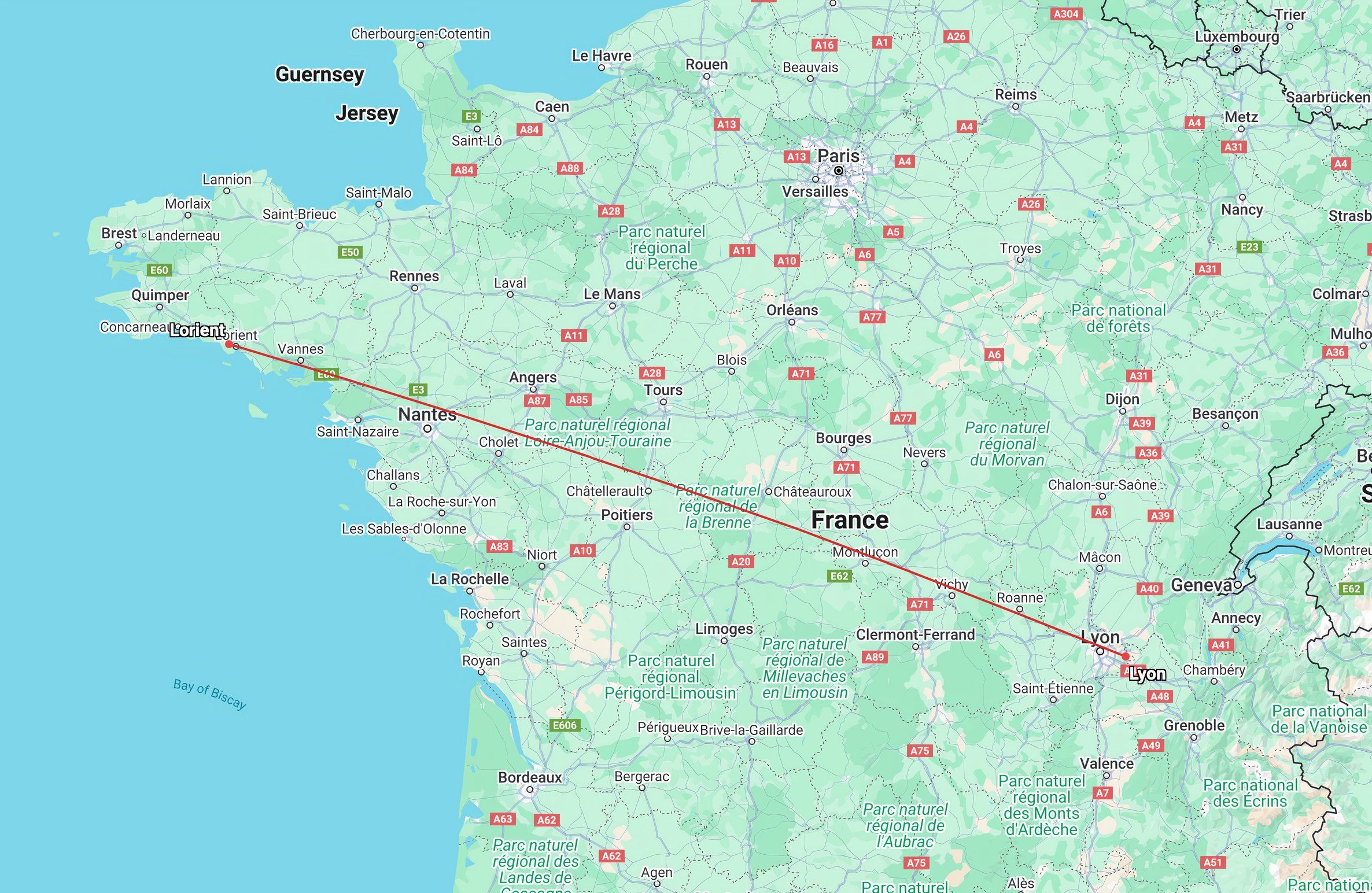
Proteus Airlines Flight 706 was scheduled as a commercial flight from Lyon to Lorient, France.
The flight was operated by a Beechcraft 1900D aircraft
, a twin-engine turboprop known for its reliability on short regional flights. Onboard were twelve passengers and two crew members, including Captain Jean-François Palette, who had over 10,000 flight hours under his belt.
Photo: Greatcirclemaps
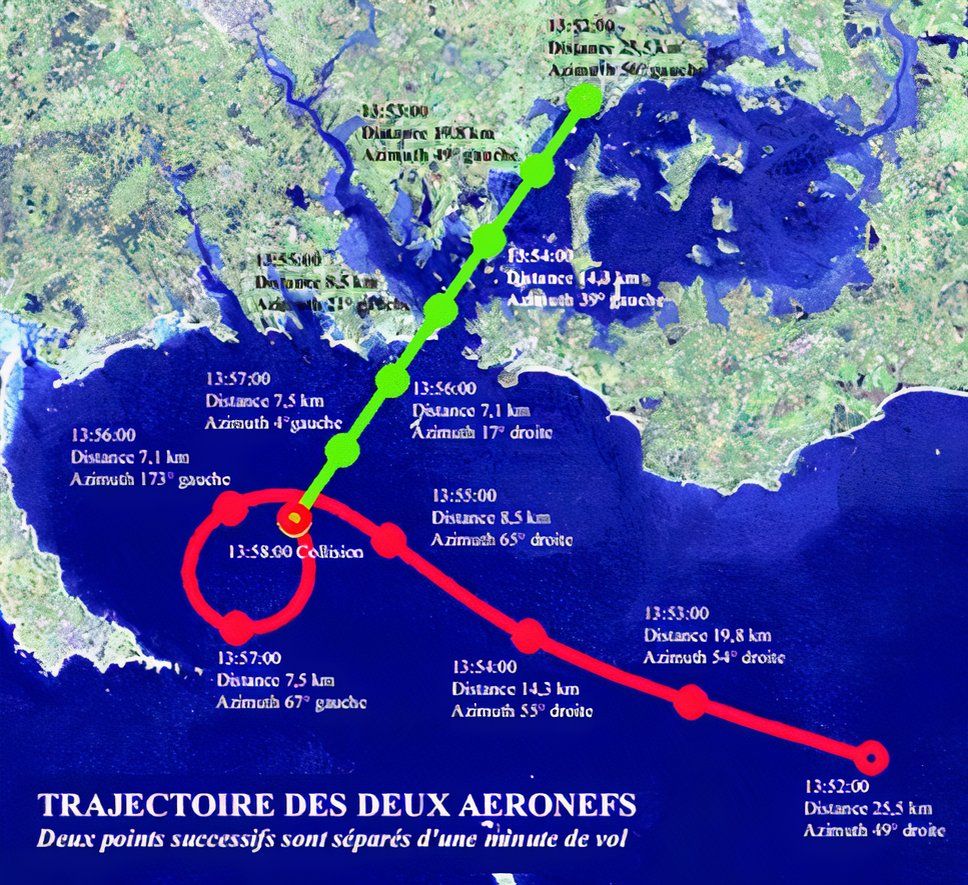
After consulting with his co-pilot, the flight was progressing smoothly until Captain Palette decided to take a brief deviation over Quiberon Bay to give the passengers a view of the SS Norway, a famed cruise ship anchored in the bay. This decision, however well-intentioned, would prove disastrous. According to Smithsonian Magazine, the deviation was a minor sightseeing opportunity without alerting air traffic control (ATC), leaving nearby aircraft unaware of the sudden change in the Beechcraft’s flight path.
The collision: a fatal miscalculation
While Flight 706 descended for a closer view of the SS Norway, a privately owned Cessna 177 flew nearby. The Cessna pilot, Jean-Paul Gervais, had taken off from Vannes with a single passenger for a casual sightseeing trip over the bay. Crucially, the Cessna and the Beechcraft were not in communication, and neither pilot was aware of the other aircraft’s proximity.
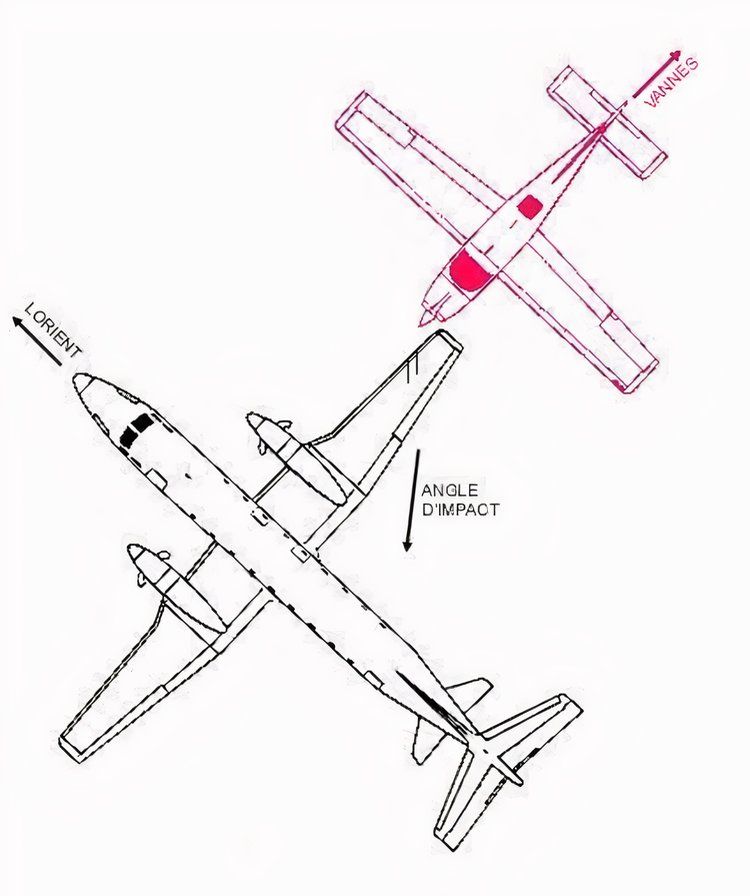
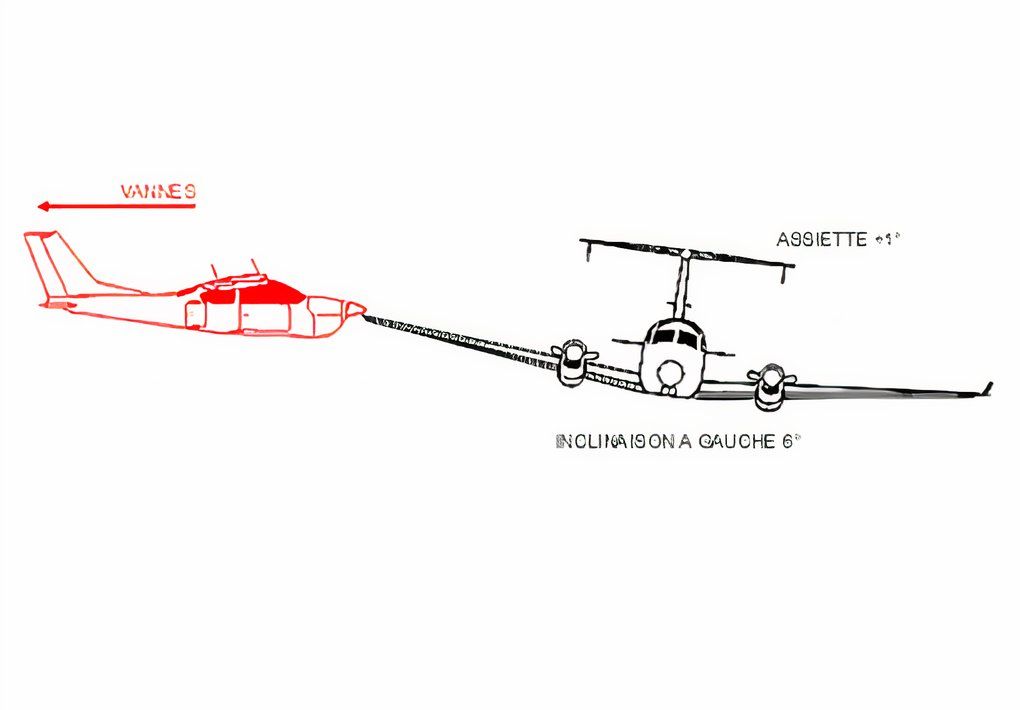
As reported by Aviation Safety Network, at around 2,000 feet, the Proteus flight descended directly into the Cessna’s flight path. In a devastating instant, the Beechcraft’s left wing struck the Cessna, severing it upon impact. Both aircraft were critically damaged, leading to a complete loss of control.
Get up to date with all the latest aviation news right here on Simple Flying!
The Beechcraft 1900D rapidly broke apart and fell into the sea below, while the Cessna also plummeted, leaving no chance of survival for those onboard. All fourteen people in both aircraft were killed almost instantly, marking the end of what was supposed to be a routine flight and a casual sightseeing journey.
The investigation: analyzing the cause
In the wake of the collision, French aviation authorities launched an exhaustive investigation. According to Wikipedia, the primary focus was on the unexpected deviation made by the Beechcraft’s captain. Although such detours were not entirely uncommon on regional flights, the captain’s failure to notify ATC or request clearance for the altered route proved to be a critical error.
ATC was unaware of the Beechcraft’s intention to descend and thus could not alert other aircraft to its presence. Further findings, as detailed on Reddit’s r/aircrashinvestigation forum, revealed that the Proteus Airlines crew had operated under the assumption that the airspace over Quiberon Bay was clear.

Related
What Are The Most Important Stages In An Air Crash Investigation?
Air crash investigations are paramount in order to discover the cause of the crash and correct future incidents. let’s discover the steps.
In reality, this region of airspace saw frequent low-altitude traffic, especially private aircraft on sightseeing flights. The investigation highlighted that although Captain Palette was highly experienced, his decision to deviate was poorly timed and executed without sufficient situational awareness.
A deadly decision
As investigators delved more profoundly, the human factor emerged as the most significant element in the tragic equation. According to Smithsonian Magazine, the captain’s decision to descend for sightseeing, though motivated by a desire to offer passengers a memorable experience, violated standard safety protocols. Deviating from a planned route without notifying ATC creates an unpredictable situation in the airspace, which proved catastrophic.
Photo: Konwicki Marcin | Shutterstock
This choice also highlighted the psychological phenomenon of “expectation bias.” According to SkyBrary, an expectation bias occurred when the captain may have underestimated the risk due to familiarity with the airspace. As an experienced pilot, he likely assumed that a brief, unannounced deviation would be safe in the sparsely populated skies over Quiberon Bay. Unfortunately, this assumption collides with the reality of shared airspace, resulting in fatal consequences.
Similar midair collisions that have occurred in the past two decades:
|
Date |
Location |
Aircraft Involved |
Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
|
July 1, 2002 |
Überlingen, Germany |
Bashkirian Airlines Tupolev Tu-154 and DHL Boeing 757 |
The two aircraft collided at 35,000 feet due to miscommunication between air traffic control and the aircraft’s collision avoidance systems, resulting in 71 fatalities. |
|
September 29, 2006 |
Amazon Rainforest, Brazil |
Gol Transportes Aéreos Boeing 737 and Embraer Legacy 600 |
A midair collision occurred at 37,000 feet due to a combination of air traffic control errors and transponder issues, leading to the loss of 154 lives on the Boeing 737. |
|
August 27, 2006 |
Khartoum, Sudan |
Sudan Airways Airbus A310 and Sudanese Air Force An-26 |
The two aircraft collided on the runway during landing and takeoff operations, resulting in the destruction of both aircraft and multiple fatalities. |
|
October 12, 2011 |
Buenos Aires, Argentina |
Sol Líneas Aéreas Saab 340 and private Piper PA-28 |
The aircraft collided in midair during approach to Buenos Aires, leading to the deaths of all 22 occupants on the Saab 340 and the pilot of the Piper PA-28. |
|
March 5, 2024 |
Nairobi, Kenya |
Safarilink Aviation Dash 8 and Cessna 172 |
Shortly after takeoff, the two aircraft collided over Nairobi National Park. The Dash 8 managed to land safely with no injuries, but the Cessna crashed, resulting in the deaths of both occupants. |
Regulatory changes and safety protocols
In response to this tragic collision, aviation authorities in France and Europe examined safety protocols surrounding low-altitude, high-traffic areas where commercial and private aircraft might share airspace. Aviation Safety Network reported that subsequent changes emphasized the importance of strict adherence to flight plans, especially for commercial flights.
It reinforced the requirement for ATC coordination during any unplanned route deviations.
Photo: Richard Thornton | Shutterstock
Additionally, awareness of TCAS technology grew significantly after this accident. Although neither the Beechcraft nor the Cessna was mandated to have TCAS, the incident underscored the benefits of collision-avoidance technology for commercial and private aviation. Today, TCAS is widely mandated for commercial aircraft, significantly reducing the likelihood of similar midair collisions.

Related
New Report: Explosive Materials Traces Found In Remains Of Deadly 2016 Egyptair Airbus A320 Crash
However, the BEA disputed the claims that there was an onboard explosion.
Remembering flight 706
The story of Proteus Airlines Flight 706 remains a sad reminder of the risks accompanying even minor deviations in the carefully orchestrated world of aviation. The accident significantly underscores the critical nature of communication between pilots and air traffic controllers when deviating from planned flight paths.
Moreover, the tragedy reflects the human cost of lapses in situational awareness, even among experienced pilots. It serves as a cautionary tale for the importance of vigilance, adherence to established safety protocols, and the potential impact of overconfidence in familiar surroundings.